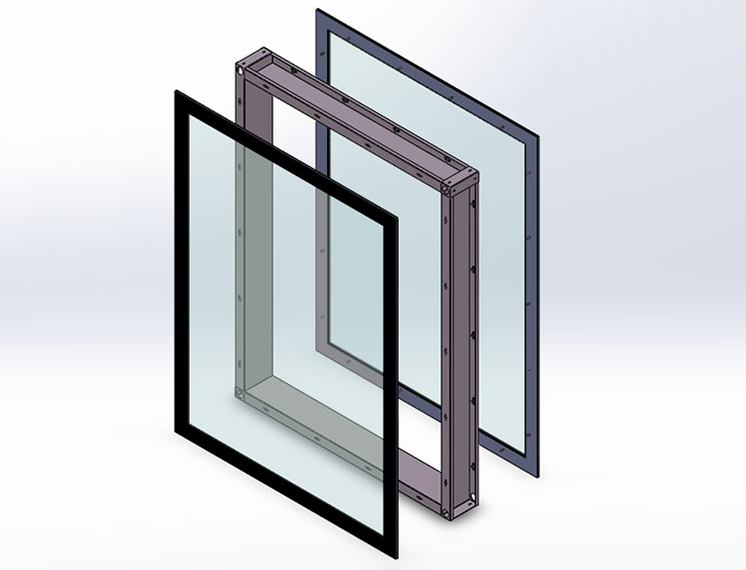
The sealing materials used in steel cleanroom doors are crucial for maintaining a tight barrier against contaminants and ensuring the integrity of the controlled environment. The most common sealing materials are selected for their durability, flexibility, resistance to contamination, and ease of cleaning. Here are the most commonly used materials and the reasons for their selection:
1. Silicone Rubber
Why it’s used: Silicone rubber is one of the most popular materials for cleanroom door seals due to its excellent flexibility, high-temperature resistance, and ability to form tight, long-lasting seals. It can maintain its elasticity and performance over a wide range of temperatures (from -60°C to 250°C), which makes it suitable for environments with varying temperature conditions.
Advantages:
Non-reactive, reducing the risk of contamination.
Resistant to aging, UV light, and ozone, ensuring long-term performance.
Can maintain a tight seal, even with slight door frame misalignment.
2. EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) Rubber
Why it’s used: EPDM is known for its excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and UV exposure. It is also highly resistant to water and chemicals, making it a good choice for environments where cleanliness and chemical resistance are essential.
Advantages:
Offers superior sealing properties and is highly durable.
Resistant to water and moisture, which is important in cleanrooms with high humidity levels.
Does not contribute to contamination and is chemically inert.
3. Polyurethane
Why it’s used: Polyurethane seals are flexible, durable, and resistant to wear and tear. It’s a preferred material when a cleanroom requires a combination of chemical resistance and resilience under heavy traffic conditions.
Advantages:
High abrasion resistance, making it ideal for high-traffic areas.
Resistant to chemicals and oils, which can be beneficial in industries like pharmaceuticals and electronics.
Provides a long-lasting, tight seal that prevents particle ingress.
4. Neoprene
Why it’s used: Neoprene is a synthetic rubber that offers good resistance to weathering, oils, and some chemicals. It is often used for general cleanroom applications where environmental factors such as humidity or chemical exposure are less extreme.
Advantages:
Provides a durable, flexible seal that resists tearing.
Good resistance to oil, heat, and ozone, making it suitable for environments with moderate temperature or chemical exposure.

5. Teflon (PTFE)
Why it’s used: Teflon is used in high-performance sealing applications, especially when extreme resistance to chemicals, heat, and abrasion is needed. It is non-stick, which reduces the build-up of contaminants on the seals.
Advantages:
Extremely resistant to chemical degradation and heat.
Non-stick properties prevent particles from adhering to the seal, which helps maintain the cleanliness of the door.
Excellent for use in highly controlled cleanroom environments where minimal contamination is crucial.
6. Viton
Why it’s used: Viton seals are made from fluorocarbon rubber, which is known for its high resistance to chemicals, extreme temperatures, and pressure. This material is ideal for cleanrooms in industries dealing with highly reactive chemicals, such as pharmaceuticals or biotechnology.
Advantages:
Highly resistant to corrosive chemicals and extreme temperatures.
Long-lasting performance even in harsh environments.
Suitable for critical cleanroom applications requiring tight seals and chemical resistance.
7. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Why it’s used: PVC is used in some cleanroom applications due to its balance of cost and performance. It is flexible and can be molded into various shapes to create effective seals.
Advantages:
Affordable compared to other high-performance sealing materials.
Suitable for low- to medium-performance cleanrooms.
Can be used in a variety of environmental conditions, though it is not as heat- or chemical-resistant as other options.
Factors Influencing Seal Material Selection:
Cleanroom Class and Industry Standards: Different industries (pharmaceutical, semiconductor, aerospace, etc.) require different sealing materials based on their cleanliness requirements.
Chemical Exposure: For cleanrooms that handle chemicals, materials like Viton, EPDM, and Teflon are preferred for their chemical resistance.
Temperature Range: Silicone and EPDM are often chosen for cleanrooms with temperature variations, as they can handle both high and low extremes.
Durability and Traffic: Materials like polyurethane and neoprene are ideal for cleanrooms with heavy foot or equipment traffic due to their abrasion resistance.
Ease of Cleaning: Seals made from non-porous materials like Teflon or silicone are easier to clean and maintain, helping to prevent particle accumulation on the seals.

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español